QuikSCAT
QuikSCAT (Quik SCATterometer) is a satellite launched by the NASA the 19th of June 1999. The onboard SeaWinds instrument is a rotating scatterometer designed for the measurement of the surface wind speed and direction over the ocean. Thanks to its higher resolution and its wider sample pattern, value-added products with higher time and space resolution, compared to ERS, can be generated. These data are used daily in weather forecasting models and have many application in ocean research.
SeaWinds
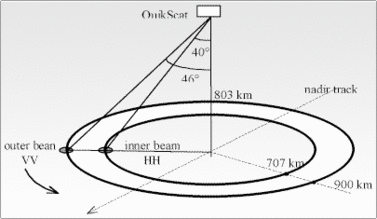
The SeaWinds on QuikSCAT sensor is a Ku band scatterometer operating at 13.46 GHz, using a 1-meter-diameter rotating disk that produces two spot beams, sweeping in a circular pattern. The incidence angles are respectively 46° and 54° for the inner and outer beams. The satellite altitude is about 800 km; swath is 1800 km large for the outer beam and 1414 km for the inner beam. The polarisation is horizontal for the inner beam and vertical for the outer beam. For each 25 x 25 km cell, called Wind Vector Cell (WVC), SeaWinds measures up to 42 Sigma0 which are used to retrieve the 10 meters surface wind (module and direction).
Additional Info
- Mission: QuikSCAT
- Agency: NASA
- Orbit: polar
- Launch date: Monday, 19 July 1999
- Status: operational
- Mission end: Monday, 23 November 2009